Embedded Systems: History
History of Embedded Systems
In the older days Embedded Systems were built around the old vacuum tube and transistor technologies and the embedded algorithms were developed in low-level languages. Advances in semiconductor and nano-technology and the IT revolution gave a thrust to the development of miniature embedded systems.
APOLLO GUIDANCE COMPUTER (AGC)
- First recognized modern embedded system is the APOLLO GUIDANCE COMPUTER (AGC) developed by the MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Instrumentation Laboratory for the Lunar Expedition.
- The AGC Inertial Guidance Systems ran for both the Command Module (CM) and the Lunae Excursion Module (LEM).
- The Command Module was designed to encircle the moon while the Lunae Excursion Module and its crew members were go down to the moon surface and land there safely.
- 18 engines were included in the Lunar Module. There were 16 reaction control thrusters, a descent engine and an ascent engine. The descent engine was designed to provide thrust to the Lunar Module out of the lunar surface and land it safely on the moon.
- MIT’s original design was based on 4K words of fixed Read Only Memory (ROM) and 256 words of Erasable Memory (Random Access Memory). By June 1963, the figures reached to 10K fixed Read Only Memory and 1K Erasable Memory. The final configuration was 36K words of fixed Read Only Memory and 2K words of Erasable Memory.
- The earliest microprocessor prototype used in AGC had a 1.024 MHz clock frequency that was obtained from a 2.048 MHz crystal clock.
- The computing unit of AGC was consisted of approximately 11 instructions and 16-bit word logic. Around 5000 ICs (3-input NOR gates, RTL Logic) supplied by Fairchild Semiconductor were used in this design.
- DSKY (Display/Keyboard) refers to the AGC’s user interface component. DSKY looked like a calculator type keypad with an array of numericals. It was used to numerically feed the commands to the module.
- Fig. 1 shows the different units developed by MIT Instrumentation Laboratory for the APOLLO GUIDANCE COMPUTER for Lunar Expedition.
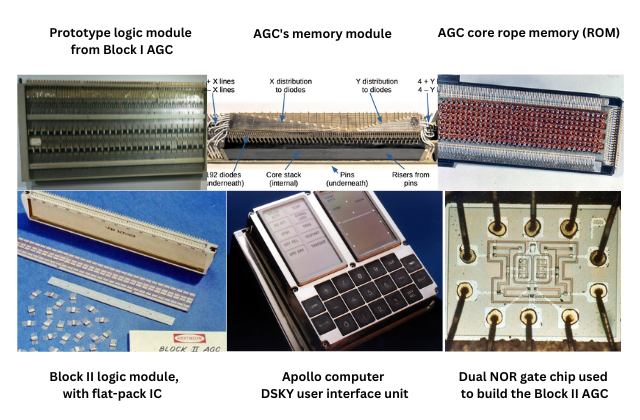
Fig. 1: Modules developed by MIT Instrumentation Lab for the AGC for Lunar Expedition
Autonetics D-17
- The first mass-production Embedded System was the guidance computer for the Minuteman-I missile in 1961.
- Discrete transistor logic was used to build the “Autonetics D-17” guiding computer, which included a hard drive for primary memory.
- Despite the fact that the first integrated circuit was created in September 1958, computers that used them didn’t start to exist until 1963.
- The first intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) to use solid fuels—which are safer and ignite more quickly than liquid fuels—was 17-metre (56-foot) in length, three-staged rocket. Moreover, it was the first American ICBM to be housed in an underground silo.
- Fig 2 shows the Minuteman-I missile and Autonetics D-17 guidance computer from a Minuteman-I missile.
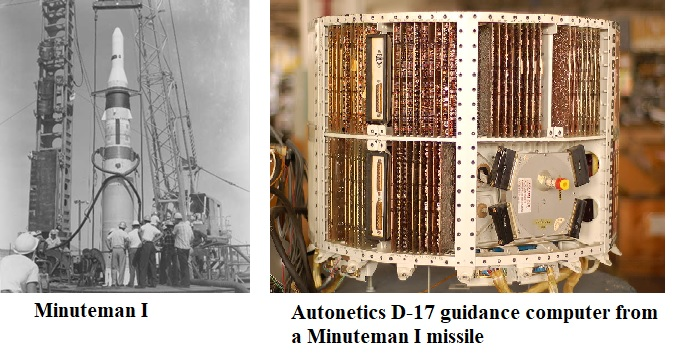
Fig 2: Minuteman-I missile and Autonetics D-17
Embedded System for Vehicle
- The Volkswagen (VW) 1600 introduced the first embedded system for a car in 1968, using a microprocessor to manage its electronic fuel injection system.
Embedded Software
- Real-time VxWorks, the first embedded operating system, was published by Wind River in 1987.
- In 1996, Microsoft released Windows Embedded CE.
- The first embedded Linux products started to appear around the late 1990s.
- Nowadays, practically all embedded devices run Linux.
