Embedded Systems: Application Areas
Applications of Embedded Systems:
Embedded systems are systems specially designed to complete a particular goal. A wide range of industries uses them, including automobiles, medical equipment, home appliances, industrial automation, and aerospace. Some of the most common applications of embedded systems include:
1. Automotive Systems:
Embedded systems play a crucial role in modern automobiles, providing a range of functions for vehicle control, communication, and entertainment. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of automotive systems:
- Engine Management: An engine control unit (ECU) monitors and controls the engine’s operation, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions. It collects data from various sensors, processes it using algorithms, and adjusts the engine’s performance accordingly.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS is an embedded system that prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, improving vehicle control and stability. It uses sensors to detect wheel speed and adjusts the brake pressure accordingly.
- Airbag Control: Airbag control systems are embedded systems that detect and deploy airbags in the event of a collision. They use sensors to detect the severity of the impact and deploy the airbags accordingly.
- In-vehicle Entertainment Systems: Modern automobiles have in-vehicle entertainment systems that include audio and video players, navigation systems, and communication systems. These systems are powered by embedded systems that control the display, user interface, and connectivity.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): ADAS systems are embedded systems that assist the driver in various ways, such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. Drivers receive alerts and assistance from the vehicle’s surroundings via various sensors, including radar and cameras.
- Telematics: Telematics systems are embedded systems that provide connectivity between the vehicle and the outside world, such as the internet, other vehicles, and infrastructure. They enable features such as remote diagnostics, vehicle tracking, and emergency services.
Embedded systems have revolutionized the automotive industry by introducing advanced features for vehicle control, safety, and entertainment. They have also enabled a new era of connected and autonomous vehicles.
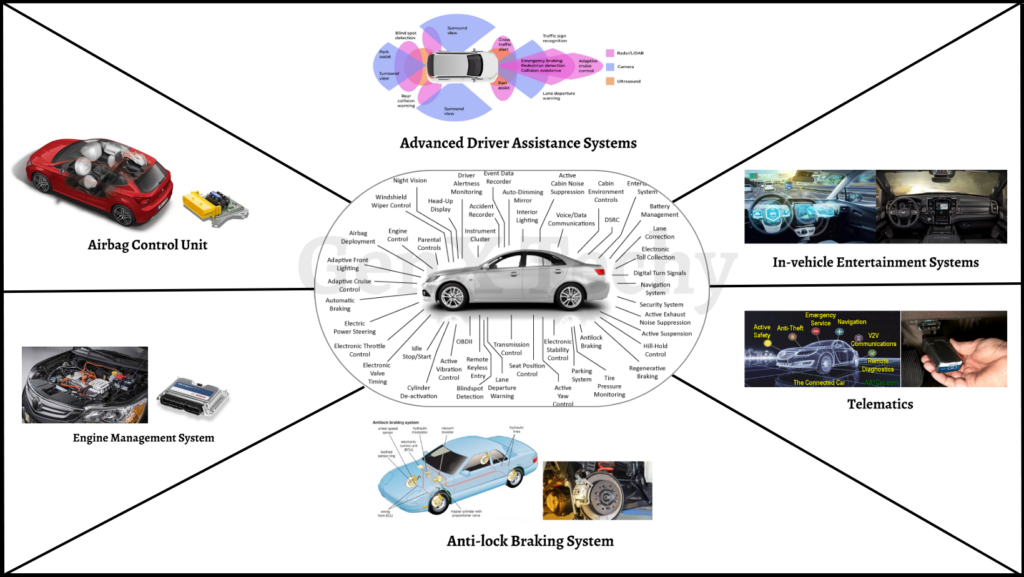
Fig 1: Embedded Systems in Automotive Systems
2. Consumer Electronics:
Embedded systems have revolutionized the consumer electronics industry, providing functionality and control for a wide range of devices. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of consumer electronics:
- Smartphones: Smartphones are powered by embedded systems that control the operating system, user interface, and connectivity. Location tracking, motion detection, and augmented reality are all tasks that embedded systems may carry out using sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS.
- Digital Cameras: Digital cameras have embedded systems that control the image processing, autofocus, and exposure settings. Additionally, they offer capabilities including video recording, facial identification, and image stabilization.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles like the Xbox and PlayStation use embedded systems that provide the game logic, graphics rendering, and user interface. They also provide connectivity for online gaming and social networking.
- Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices such as smart speakers, thermostats, and lighting systems use embedded systems that provide connectivity, user interface, and control. They can be incorporated into home automation systems and managed by voice assistants or smartphone apps.
- Wearables: Embedded systems are utilized in wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers, enabling features such as activity tracking, heart rate monitoring, notifications, etc.
- Home Entertainment Systems: Overall, embedded systems have enabled a new generation of consumer electronics devices with advanced features and connectivity, providing greater functionality, convenience, and entertainment to consumers.
The embedded systems used by home entertainment systems like televisions and soundbars offer capabilities including high-definition video playback, surround sound, and streaming services. They can be controlled through remote controls, mobile apps, or voice assistants.
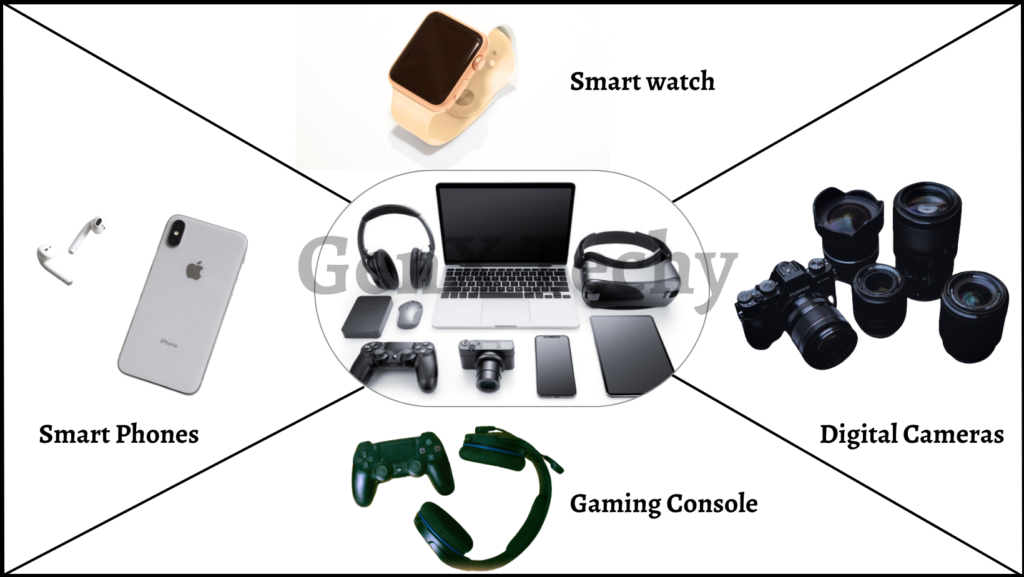
Fig 2: Embedded Systems in Consumer Electronics
3. Medical Devices:
Embedded systems play a crucial role in modern medical devices, providing advanced features for patient monitoring, treatment, and diagnostics. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of medical devices:
- Implantable Medical Devices: Embedded systems are used to operate and connect with external equipment in implantable medical devices such pacemakers, defibrillators, and neurostimulators. Their function involves monitoring various physiological parameters, such as heart rate and brain activity, and administering therapeutic interventions whenever necessary.
- Medical Imaging: Medical imaging systems such as X-ray machines, CT scanners, and MRI machines use embedded systems for image acquisition, processing, and analysis. For diagnostic and treatment purposes, they provide high-resolution images of the body.
- Patient Monitoring Systems: Patient monitoring systems such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) machines, blood glucose monitors, and pulse oximeters use embedded systems to monitor various physiological parameters and provide real-time data to healthcare professionals. In both hospital and home settings, they can be utilized to continuously monitor patients with chronic conditions.
- Infusion Pumps: Infusion pumps are medical devices that deliver medication or fluids to patients in a controlled manner. They use embedded systems to control the flow rate, volume, and timing of the infusion, ensuring accurate and safe delivery of medication.
- Respiratory Devices: Respiratory devices such as ventilators, CPAP machines, and oxygen concentrators use embedded systems to control the airflow, pressure, and oxygen concentration. They provide respiratory support for patients with respiratory conditions or during surgical procedures.
- Prosthetics: Prosthetic devices such as artificial limbs and hearing aids use embedded systems to provide functionality and control. Motion control and noise reduction can be customized according to the patient’s needs.
Overall, advanced features for patient monitoring, therapy, and diagnostics have been made possible by embedded systems, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
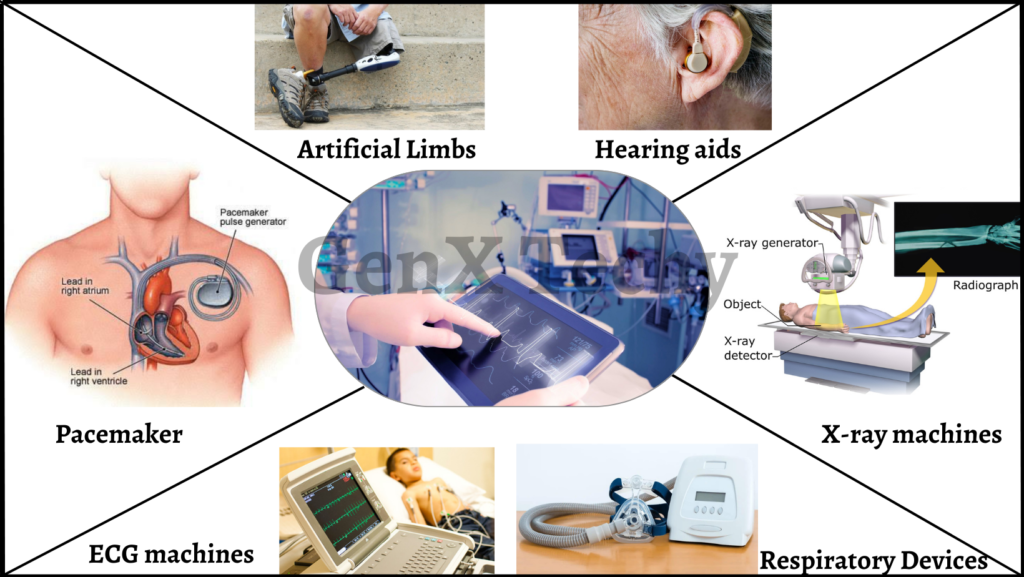
Fig 3: Embedded Systems in Medical Devices
4. Industrial Automation:
Embedded systems have revolutionized the field of industrial automation, providing advanced features for the control, monitoring, and optimization of manufacturing processes. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of industrial automation:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLCs are embedded systems that provide control for industrial processes and machines. To ensure effective and secure functioning, they keep an eye on sensors like pressure and temperature as well as control actuators like motors and valves.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): HMIs are embedded systems that provide a graphical user interface for operators to monitor and control industrial processes. They can display real-time data, such as machine status and production rates, and allow operators to adjust parameters and settings.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems: SCADA systems are embedded systems that provide centralized control and monitoring of industrial processes across multiple sites. They collect data from sensors and devices, store and analyze it, and provide insights for optimization and troubleshooting.
- Industrial Robotics: Industrial robots are embedded devices that automate tasks like welding, painting, and assembly in the production process. They can be programmed to carry out sophisticated operations with extreme accuracy and effectiveness, enhancing output and caliber.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems are embedded systems that use machine learning algorithms to analyze data from sensors and devices to predict when maintenance is needed. They can detect potential issues before they become critical and help prevent unplanned downtime.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IIoT is a network of embedded systems that connect industrial devices and machines, allowing real-time data collection and analysis. It enables advanced features such as predictive maintenance, remote monitoring and control, and machine learning-based optimization.
Overall, embedded systems have transformed industrial automation, providing advanced features for the control, monitoring, and optimization of manufacturing processes, and enabling a new era of intelligent and connected factories.
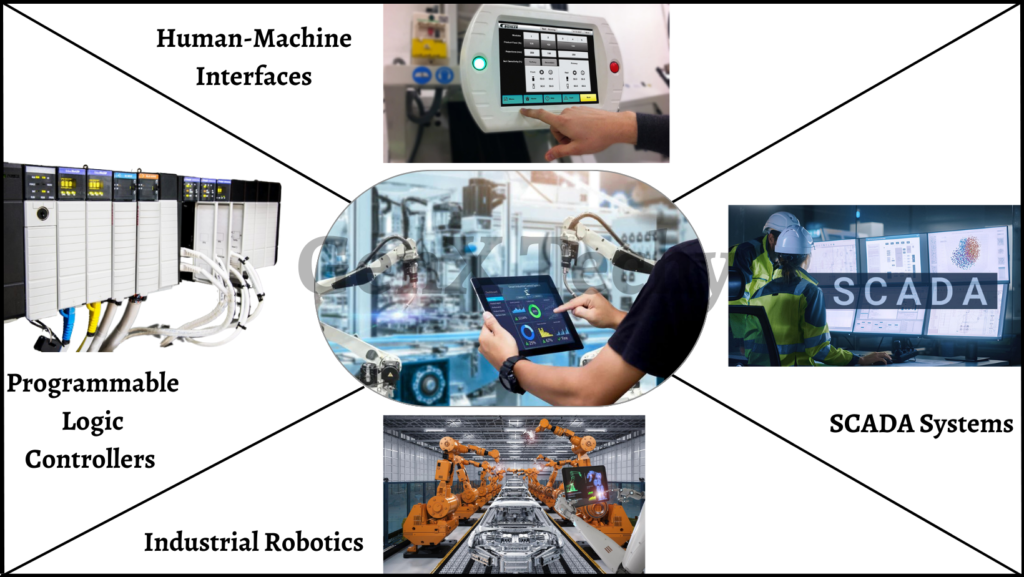
Fig 4: Embedded Systems in Industrial Automation
5 . Aerospace and Defence:
Embedded systems have played a crucial role in the aerospace and defense industries, providing advanced features for communication, navigation, and control of aircraft and spacecraft. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of aerospace and defense:
- Avionics: Avionics are the electronic systems used in aircraft, such as flight control, navigation, communication, and monitoring systems. They use embedded systems for real-time data processing and communication with ground-based control systems, ensuring safe and efficient flight operations.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): UAVs, also known as drones, use embedded systems for control, navigation, and communication. They can be remotely controlled or autonomous and utilized for a variety of tasks like reconnaissance, surveillance, and aerial photography.
- Satellite Systems: Satellites use embedded systems for communication, navigation, and imaging purpose. They can provide global coverage and are used for various applications, such as weather forecasting, earth observation, and communication.
- Defence Systems: Defence systems, such as radar systems, missile guidance systems, and electronic warfare systems, use embedded systems for real-time data processing and control. They provide situational awareness and defense capabilities for military operations.
- Spacecraft Systems: Spacecraft systems, such as guidance, navigation, and control systems, use embedded systems for real-time data processing and communication with ground-based control systems. They guarantee the spacecraft’s efficient and safe operation during launch, orbit, and return.
- Cockpit Displays: Cockpit displays use embedded systems for real-time data processing and presentation to pilots. They can offer sophisticated functions like terrain awareness and collision avoidance, as well as display several types of information like navigation data, engine performance, and weather information.
As a whole, embedded systems have enabled the aerospace and defense industries to add cutting-edge features and capabilities, improving flight efficiency, safety, and performance.
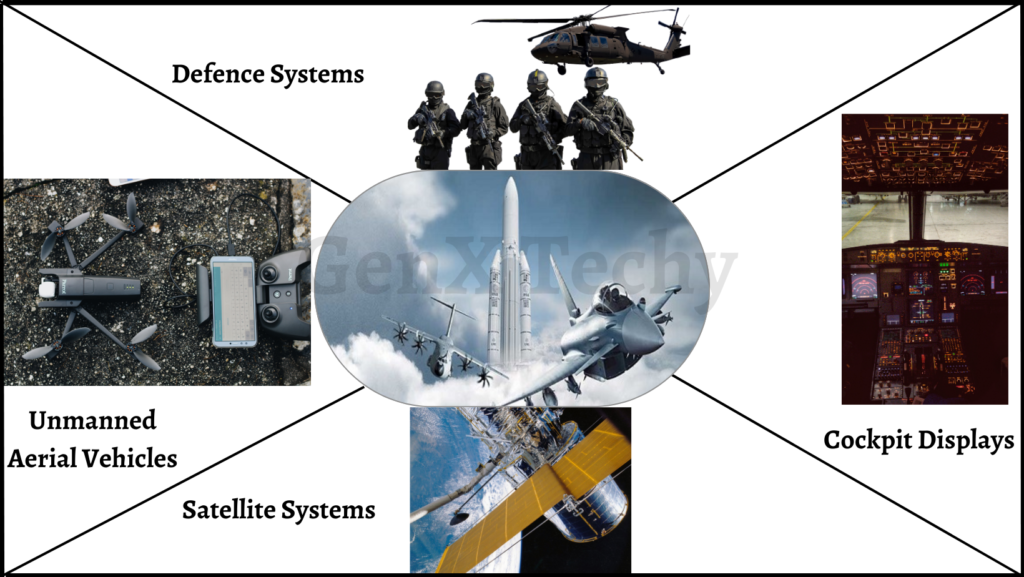
Fig 5: Embedded Systems in Aerospace and Defence
6. Home Automation:
Embedded systems have revolutionized the field of home automation, providing advanced features for the control, monitoring, and optimization of various home systems. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of home automation:
- Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices, such as smart thermostats, smart locks, and smart lights, use embedded systems for control and communication. They can be remotely controlled through mobile apps and provide advanced features, such as energy efficiency and security.
- Home Entertainment Systems: Home entertainment systems, such as home theaters and sound systems, use embedded systems for control and optimization. They can provide advanced features, such as voice control and personalized settings.
- Security Systems: In real-time monitoring and alerting, security systems, such as video cameras and motion detectors, use embedded systems. They can provide remote access and control and improve home security and safety.
- Energy Management Systems: Energy management systems use embedded systems for monitoring and optimization of energy usage. They can manage heating, cooling, and lighting systems by lowering energy costs and boosting energy efficiency.
- Home Healthcare Systems: Home healthcare systems, such as remote patient monitoring devices, use embedded systems for data collection and communication. They can offer real-time monitoring and communication with medical staff, enhancing patient care and safety.
- Kitchen Appliances: Kitchen appliances, such as smart ovens and refrigerators, use embedded systems for control and optimization. They can provide advanced features, such as remote control and energy efficiency.
Overall, embedded systems have transformed home automation, providing advanced features for the control, monitoring, and optimization of various home systems. They enable more efficient, convenient, and secure home environments and improve the quality of life for homeowners.
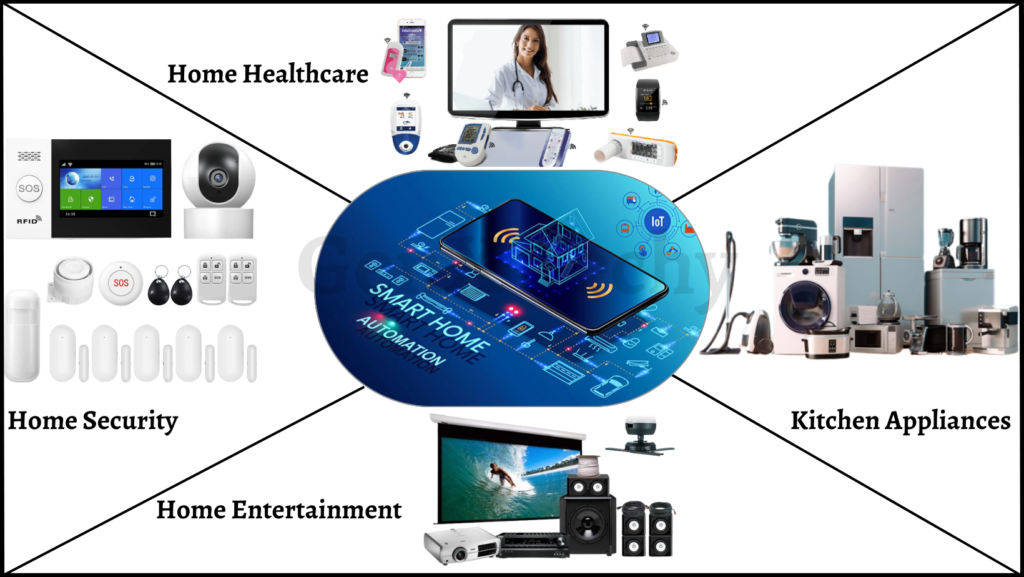
Fig 6: Embedded Systems in Home Automation
7. Gaming and Entertainment:
Embedded systems play a vital role in the gaming and entertainment industry, providing advanced features for game development, graphics rendering, and user interaction. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of gaming and entertainment:
- Game Consoles: Game consoles, such as PlayStation and Xbox, use embedded systems for graphics rendering, user interface, and game control. Advanced elements like internet gaming and social interaction are offered along with high-quality gaming experiences.
- Handheld Gaming Devices: Handheld gaming devices, such as Nintendo Switch and Sony PlayStation Portable, use embedded systems for graphics rendering, touchscreen control, and wireless communication. They provide portable gaming experiences with advanced features, such as multiplayer gaming and internet connectivity.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual and augmented reality systems use embedded systems for real-time data processing and graphics rendering. The technology provides immersive experiences that incorporate advanced features, such as 3D modeling, tracking, and motion detection.
- Sound and Music Systems: Sound and music systems, such as headphones and speakers, use embedded systems for sound processing and optimization. With cutting-edge technologies like wireless networking and noise cancellation, they offer premium audio experiences.
- Set-Top Boxes: Set-top boxes, such as Apple TV and Amazon Fire TV, use embedded systems for multimedia playback and streaming. They provide advanced features, such as online streaming and voice control, for a seamless entertainment experience.
- Gaming Peripherals: Gaming peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, and gamepads, use embedded systems for control and optimization. They provide advanced features, such as customizable keys and wireless connectivity, for a better gaming experience.
Overall, embedded systems have enabled a new era of advanced gaming and entertainment experiences, providing high-quality graphics, sound, and user interaction. They have transformed the way we play games and consume multimedia, making it more immersive and interactive.
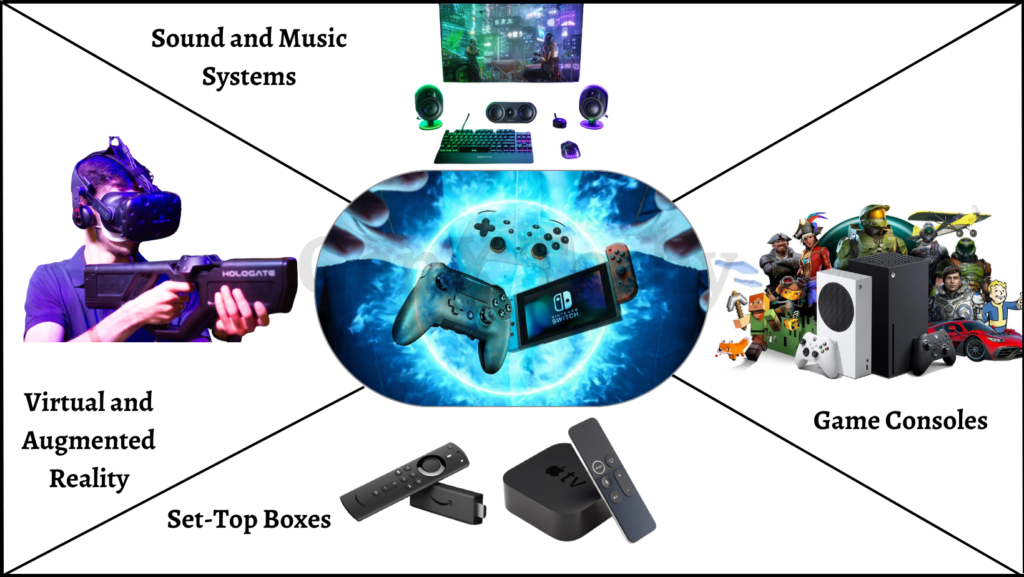
Fig 7: Embedded Systems in Gaming and Entertainment
8. Energy Management:
Embedded systems play a critical role in energy management, which involves monitoring and controlling the consumption of energy in various applications. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of energy management:
- Smart Grids: Embedded systems are used in smart grids to optimize energy distribution, manage power quality, and monitor energy consumption. These systems can detect faults in the grid and quickly isolate affected areas to prevent outages. They can also balance the energy supply and demand to avoid overloading the grid and ensure an uninterrupted power supply.
- Building Automation Systems: Embedded systems are used in building automation systems to control HVAC systems, lighting, and other energy-consuming devices. To maximize energy usage and minimize waste, these systems can modify the temperature and lighting based on occupancy levels, the time of day, and other variables.
- Industrial Automation: Embedded systems are used in industrial automation to monitor and control energy consumption in manufacturing processes. These systems can optimize energy use by adjusting the production process based on real-time energy demand, reducing energy consumption during idle periods, and scheduling maintenance activities to prevent energy waste.
- Renewable Energy: Embedded systems are used in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to control energy production and storage. These systems can monitor energy production and adjust the output based on weather conditions and energy demand. They can also manage energy storage systems to ensure that excess energy is stored efficiently and used when needed.
Overall, embedded systems are essential for energy management because they optimize energy use, cut waste, and raise the effectiveness of energy systems.
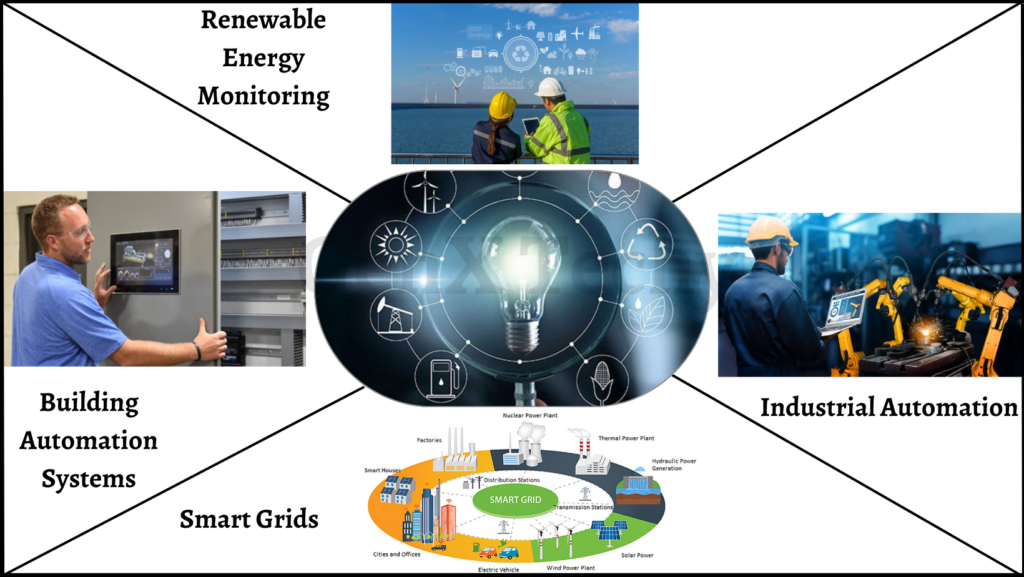
Fig 8: Embedded Systems in Energy Management
9. Communication Systems:
Embedded systems are widely used in communication systems to enhance the efficiency and reliability of data transmission. Here are some examples of embedded systems applications in the field of communication systems:
- Wireless Communication: Embedded systems are used in wireless communication devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, to enable wireless connectivity. To ensure seamless connectivity between devices, these systems can handle several wireless protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC.
- Network Routers and Switches: Embedded systems are used in network routers and switches to manage data traffic and ensure that packets are transmitted efficiently. These systems can manage routing tables, analyze network traffic, and optimize data transmission to reduce latency and improve network performance.
- Satellite Communication: Embedded systems are used in satellite communication systems to manage data transmission between satellites and ground stations. To provide secure and dependable communication, these systems can handle data encryption and decryption as well as manage sophisticated protocols like TCP/IP.
- Mobile Communication: Embedded systems are used in mobile communication systems, such as cellular networks, to manage data transmission and voice calls. These systems can manage signal strength, handovers, and roaming to ensure seamless communication between mobile devices.
Overall, embedded systems play a critical role in communication systems by optimizing data transmission, enhancing reliability, and improving network performance.
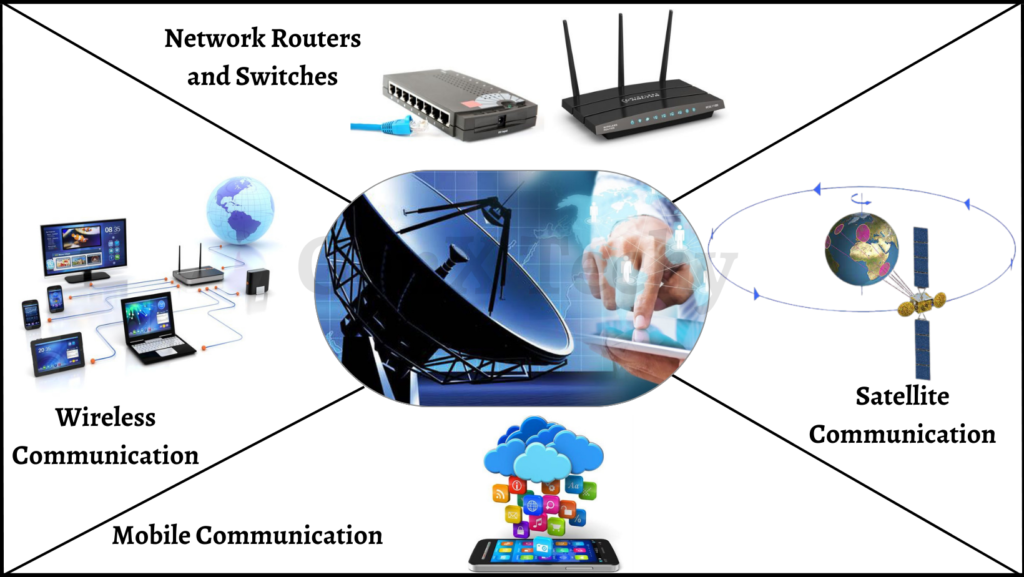
Fig 9: Embedded Systems in Communication
Modern technology cannot function without embedded systems, which allow a variety of goods and systems to carry out complicated tasks more effectively, consistently, and precisely.
